As part of a USAID project, Abhishek Srivastava worked in Kabul, Afghanistan on AMDEP (Afghanistan Media Development and Empowerment Program). The principal goal of the project is to train and assist Afghan journalists and students of Kabul University on the nuances of reporting. Abhishek tells us stories of people and places in Kabul using his photos as a medium. This is the second in a series of photo-essays on Kabul.
Part I can be accessed here: Stories from Kabul – Part I
Part II can be accessed here: Stories from Kabul – Part II
_____________________________________________________________________________
By Abhishek Srivastava, 17 Feb, 2012
1. Your Country Needs YOU!

A poster calling people to join the Afghan National Army and be a hero.
_____________________________________________________________________________
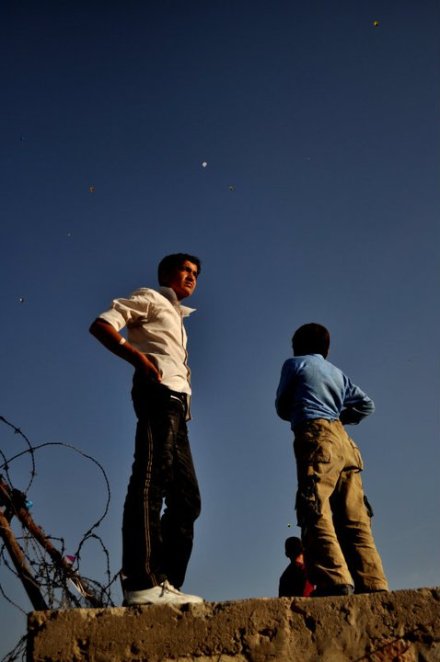
2. The Kite Runners
 Kite flying at dawn. I was not aware that kite flying is so popular among Afghans. Kite flying had been banned during the the Taliban regime.
Kite flying at dawn. I was not aware that kite flying is so popular among Afghans. Kite flying had been banned during the the Taliban regime.
3.

Bullet ridden walls and barbed wires are common in this area around Zahir Shah’s tombstone, a typical Kabul suburb. I saw hundreds of people scattered over a limitless piece of land, flying colorful kites.
4.

Keeping a hawk eye. The number of kite catchers were the same as the number of people flying the kites.
_____________________________________________________________________________
5. Baaz

That is a Baaz (Falcon). In Afghanistan, keeping of birds as pets has long been a popular pastime.
_____________________________________________________________________________
6. The River of Poppies

The main river of eastern Afghanistan is this famous Kabul River. It is a 700kms long river, and it flows east past Kabul and Jalalabad, north of the Khyber Pass into Pakistan, and past Peshawar; it joins the Indus River northwest of Islamabad. Alexander the Great used it to invade India in the 4th century BCE. It now mainly helps in the cultivation of poppies.
_____________________________________________________________________________
7. The Corner of a Foreign Field

‘Jumma Cricket in Kabul’
At 6am one day, I got a call from an Afghan asking me to accompany him to see what some Afghans do on a holiday morning, after their morning prayers.
And here I was, right in the middle of some mountains, with the wind blowing away the clouds and making way for the clear blue sky. On a ground full of rock and pebbles, with spectators sitting right next to the batting wicket, a match of cricket was on.
The ground was yet again a part of Soviet recreation facility built in the 1980’s. I could not have been more delighted, for it was the World Cup season, and India was in the finals. That was reason enough for me to connect with any match of cricket.
Out of nowhere, I got that extra adrenaline rush to hold the bat and try those rusted strokes from childhood. But first I had to watch. Yes, the cricket fever was on in Afghanistan as well. Being a holiday in this Islamic country, playing cricket every Friday is like a ritual for most. I saw some of them wearing the Pakistan cap as well.
It was 12 over match with 11 players in each team. Some of the them even tried enacting Shahid Afridi, their hero. Afridi is a popular Pakistani batsman. The moment they got to know that an Indian was present, they congratulated me for defeating Pakistan in the World Cup Semi Final and handed me the bat!
8.

Our cricket ball was a normal tennis ball, which was nicely wrapped in white plastic tape. They say that it makes the ball heavier and makes it swing, much like a leather ball. Well it did hit me hard a couple of times!
9.

Firing star batsman, Haaseeb.
_____________________________________________________________________________
10. Taimani Fort

The mud walled Taimani Fort. This fort was built in the late 1880’s. It belongs to a tribe called ‘Taimani’ in Afghanistan. I am told that underneath this fort runs a Cavernous hall and a lot of debris from the Soviet era.
_____________________________________________________________________________
The copyright of all photos are with Abhishek Srivastava. Please do not reprint without permission.